OpenAI Goes Vertical; Anthropic Chills Hype; Two Robots Talking

Today's AI Outlook: 🌤️
OpenAI Stops Renting the Future and Starts Building It
OpenAI is apparently done playing nice inside other people’s ecosystems. According to Bloomberg and the Financial Times, the company is no longer Apple’s custom model provider and is instead building a full U.S.-based AI hardware and robotics supply chain. That includes domestic silicon, motors, actuators, cooling systems and data centers.
Translation: OpenAI wants to own the stack from atoms to agents.
It seems OpenAI is quietly assembling an end-to-end platform that spans consumer devices, robotics, brain-computer interfaces and hyperscale inference infrastructure.
The shift marks a strategic break from the “model-only” era and positions OpenAI as a direct competitor to Apple, Google, and Nvidia across multiple layers of the AI economy.
Why it matters
Control equals leverage. By owning hardware, manufacturing, and deployment, OpenAI reduces dependency on rivals while locking in distribution for future AI-native devices. This is Silicon Valley’s oldest move, executed at remarkable scale.
The Deets
- OpenAI is backing Merge Labs, Sam Altman’s noninvasive brain-computer interface startup, which raised $252M in seed funding. The tech uses ultrasound-based BCIs rather than implants.
- A new partnership with Cerebras will add 750MW of ultra-low-latency inference capacity through 2028 using wafer-scale chips optimized for real-time workloads.
- ChatGPT Translate launched quietly as a standalone product. No account required, supports 25 languages, and signals OpenAI testing verticalized consumer tools beyond chat.
- Developers now have access to GPT-5.2 Codex via the Responses API, expanding multimodal coding, reasoning, and security analysis with long-session endurance.
Key takeaway
OpenAI is expanding from just building intelligence to building infrastructure, devices, and interfaces to ensure that intelligence reaches users on its own terms.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Wafer-scale computing: A chip architecture where an entire silicon wafer functions as one massive processor, enabling extreme performance and low latency.
🧠 Research & Models
Anthropic Cuts AI Productivity Hype in Half After Real-World Data
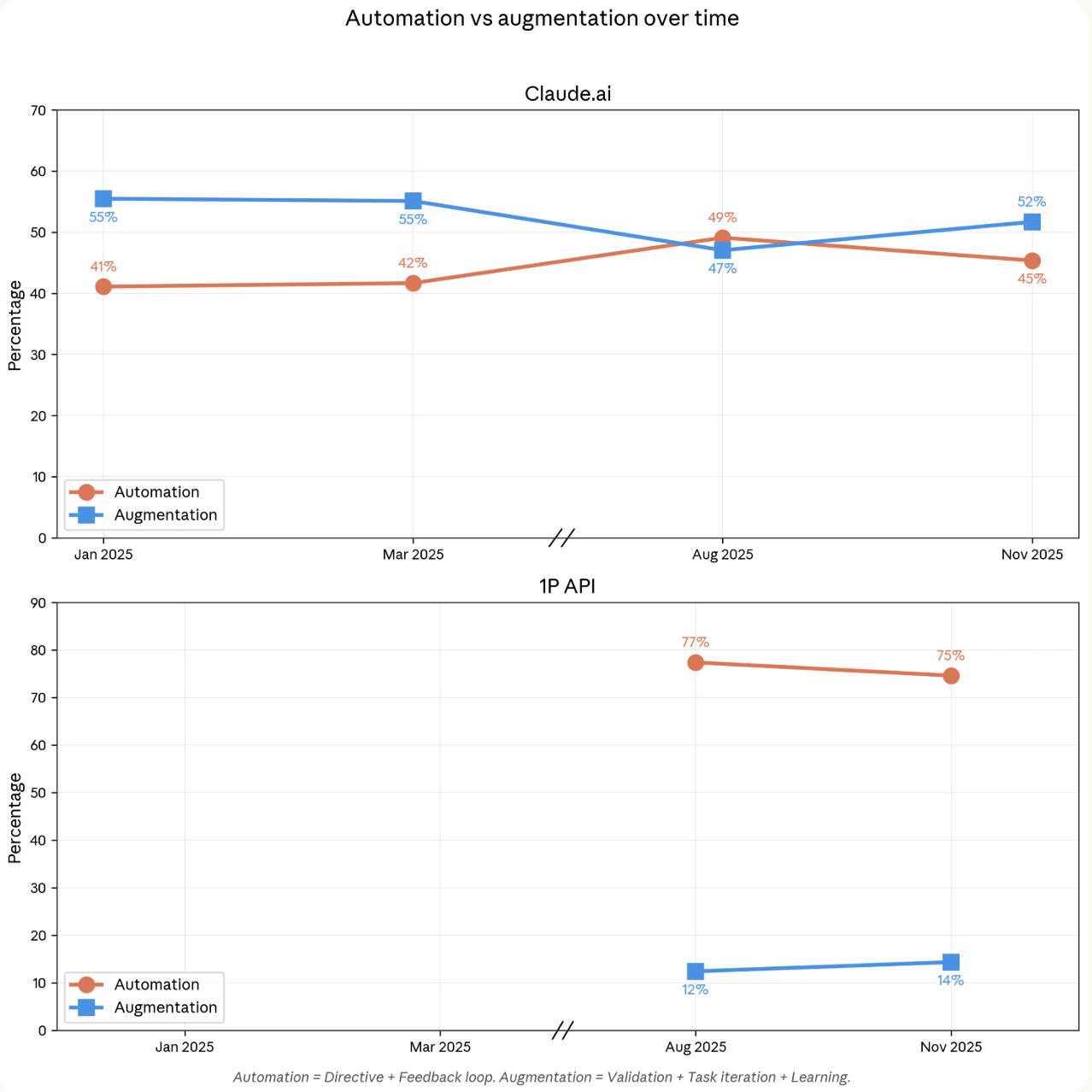
Anthropic just brought receipts. After analyzing one million real Claude conversations from November 2025, the company slashed its productivity forecasts by half. The results show AI is powerful but far less magical than early hype suggested.
Claude accelerates high-skill, college-level tasks up to 12× faster, but success rates drop as task complexity rises. Adjusted for reliability, AI could lift U.S. labor productivity by 1–1.2 percentage points annually, still meaningful but nowhere near “economic singularity” territory.
Why it matters
This is one of the first large-scale looks at how AI is actually used, not how vendors pitch it. The findings may reset expectations for policymakers, employers, and investors betting on instant productivity miracles.
The Deets
- Wealthy countries use Claude primarily for work and personal productivity; lower-income regions lean on it for education.
- Claude handles nearly half of sampled job tasks, skewing heavily toward computer science and math.
- 52% of interactions are collaborative, not fully delegated, suggesting humans still stay in the loop.
- Anthropic also upgraded Claude Code, adding MCP Tool Search with lazy loading, allowing hundreds of APIs without context bloat.
Key takeaway
AI is a force multiplier, not a replacement engine. The biggest gains come when humans and models work together.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Context bloat: When long prompts and tool histories overwhelm a model’s usable memory, reducing performance.
⚔️ Power Plays
Thinking Machines Implodes; OpenAI Reclaims the Talent
Mira Murati's Thinking Machines Lab just lost its co-founder and CTO, Barret Zoph, amid misconduct allegations. Within hours, Zoph and several others landed back at OpenAI, welcomed publicly by applications CEO Fidji Simo.
This marks the third co-founder exit in under a year for Thinking Machines, following earlier departures to Meta. Murati has since named PyTorch creator Soumith Chintala as the new CTO.
Why it matters
In AI, talent is gravity. OpenAI continues to pull experienced operators back into its orbit, even as former insiders struggle to build durable competitors.
The Deets
- Zoph was allegedly accused of sharing proprietary information with competitors.
- OpenAI had reportedly been in talks with him for weeks before the split.
- The episode underscores how fragile new AI labs remain without scale, infrastructure, and distribution.
Key takeaway
Models matter, but people still decide where power accumulates in AI.
🛠️ Tools & Products
Claude Cowork and the Collapse of the Agent Layer
Anthropic Claude Cowork just killed our startup product 😅 So we did the most rational thing: open-sourced it.
— Guohao Li 🐫 (@guohao_li) January 13, 2026
Meet Eigent 👉 https://t.co/R82WRFoh41 https://t.co/06fag6fTdk
Anthropic’s release of Claude Cowork triggered an existential moment for agent startups. Eigent, an early agent company, publicly admitted its product was dead and open sourced the code after Cowork launched. The reason was not UX, but rather platform-level integration.
Why it matters
When model providers ship native agent capabilities, standalone wrappers lose their market overnight.
The Deets
- Cowork allows parallel media tasks like image compression and audio extraction.
- Developers can connect hundreds of tools without memory penalties.
- Startups building incremental agent layers are now exposed by default.
Key takeaway
If you are not creating a new category, the platform will eventually eat you.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Agent layer: Middleware that coordinates multiple AI actions or tools on behalf of a user.
🤖 Robotics
Two Talking Humanoids Preview a Rough Cyberpunk Future
Two humanoid robots were placed face to face on a public show floor and allowed to talk freely... No scripts. No human intervention. No cloud fallback. (Kinda looked like Hall of Presidents at Disney World,)
For more than two hours, the robots, named Aria and David, carried on an unscripted, multilingual conversation in real time. The pauses, glitches, awkward timing, and misfires were not edited out. They were the point.
What unfolded was not a polished demo, but a raw exposure of what on-device embodied AI looks like today. The robots shared space, attention, and time, pushing their systems through extended interaction rather than short, controlled exchanges.
Why it matters
This is a rare look at embodied AI without theatrical framing. Most humanoid demos rely on choreography, cloud compute, or carefully staged prompts. This one did not. The result felt mechanical and imperfect, but unmistakably real. The future of humanoids is not smooth or cinematic. It is awkward, constrained, and increasingly present.
The Deets
- The robots ran fully on-device, with no cloud inference to smooth over latency or memory issues
- Extended conversation exposed limits in thermal management, memory drift, and conversational coherence
- Multilingual exchanges worked, but timing gaps and repetition surfaced quickly
- The interaction lasted long enough to stress real-world operating conditions, not just demo loops
Key takeaway
This did not feel futuristic. It felt cyberpunk. Two synthetic bodies talking in public already changes how shared spaces feel. If this trajectory continues, the future arrives unevenly, populated by machines that work well enough to be unsettling, not perfect enough to disappear.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Embodied AI: Artificial intelligence systems embedded in physical bodies that must perceive, act, and interact in real time, rather than operating purely in software or the cloud.
⚡ Quick Hits
- xAI’s Grok 4.20 reportedly discovered a new Bellman function in minutes, though still lags Claude in coding.
- GLM-Image shows open-source models can beat Google in complex visual reasoning.
- Nvidia continues to absorb TSMC capacity as Apple loses priority access.
- Microsoft unveiled OptiMind, a new optimization-focused research model on Hugging Face.
- Two humanoid robots held an unscripted, two-hour public conversation, glitches and all.
Today’s Sources: AI Breakfast, The Rundown AI, AI Secret, Robotics Herald
