Google Maps Its Route; Microsoft's 'Pre Doc'; McKinsey Bot Easily Hacked

Today's AI Outlook: 🌤️
Google Puts Gemini In The Driver’s Seat
Google’s AI strategy in 2026 has been gloriously unsubtle: put Gemini into every product people already use, then make it feel inevitable. Now it is doing that with Google Maps, rolling out Ask Maps for conversational trip planning and Immersive Navigation for 3D route visualization.
The pitch is straightforward: instead of pecking around for coffee, gas, parking, or the least-annoying route, you ask Maps like a person and get an answer like the app finally graduated from being a pinboard.
The bigger story is not just that Maps got smarter. It is that Google keeps finding high-frequency, everyday surfaces where AI can quietly become default behavior. Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Drive, Meet, Photos, Android and now Maps are all getting the same treatment. That means Google is not asking users to adopt a new AI habit from scratch. It is sliding AI into habits they already have, which is a much easier sell than “please download one more chatbot.”
Why it matters: Google’s moat is not just model quality. It is distribution. If Gemini is baked into the products billions already open by reflex, Google does not need to win every benchmark to win a lot of real-world usage.
The Deets
- Ask Maps lets users ask natural-language questions about routes and stops, pulling from 300M+ places and reviews
- Immersive Navigation renders routes in 3D, using Street View and aerial imagery to show buildings, overpasses, crosswalks, and other context
- Google also added more conversational voice guidance, Street View destination previews with parking info and clearer route trade-offs
- The rollout fits Google’s broader “Gemini everywhere” push across its consumer stack
Key takeaway: Google is turning AI into a built-in utility, not a side quest.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Distribution moat: A competitive advantage that comes from already owning the apps, platforms, or channels where people spend time, making adoption much easier.
🏛️ Power Plays
Microsoft Wants To Be Your Pre-Doc, Not Your Doctor
Microsoft just introduced Copilot Health, a new AI health experience that connects to medical records, wearable data, and lab results to help users make sense of their health information before, during, and after doctor visits.
This is Microsoft making a very specific bet: healthcare is messy, fragmented, jargon-heavy, and full of moments where people want clarity but do not necessarily need a physician on demand every second.
The company is also using unusually ambitious language around it. Microsoft AI CEO Mustafa Suleyman framed the long-term vision as a step toward “medical superintelligence,” with AI that could eventually combine the breadth of a general practitioner with the depth of a specialist. Microsoft is careful to say it is not replacing doctors, which is wise, because “your chatbot is now your cardiologist” would be a terrible launch slogan and an even worse compliance meeting.
Why it matters: This is one of the clearest examples yet of a major tech company trying to make AI useful in a high-stakes category without pretending humans are optional. If Microsoft can make health data more legible and actionable, it could become a meaningful layer between patients and the healthcare system.
The Deets
- Copilot Health connects to 50+ wearables, EHR records from 50K+ U.S. hospitals, and Function lab results
- It delivers personalized insights to help users interpret health data and prepare for doctor consultations
- Microsoft says answers are grounded in information from credible sources such as Harvard Health, with links back to sources
- The company says connected data is not used for training, and users can disconnect sources and delete linked data
Key takeaway: Microsoft is not trying to replace the doctor’s office. It is trying to become the smartest waiting room companion on earth.
🧩 Jargon Buster - EHR: Electronic health record, the digital version of a patient’s medical history used by hospitals and clinics.
AI’s Image Problem Is Getting Harder To Spin
Two narrative threads collided this week. First, Sam Altman argued that AI has become unpopular in the U.S., saying the technology is getting blamed for electricity price spikes and layoffs. Second, public-facing and enterprise AI stories keep adding fuel to the skepticism: defense ties, giant data center buildouts, layoffs linked to automation, and security failures that make “trust us” sound increasingly undercooked.
That growing discomfort is not just vibes. It is the consequence of AI shifting from speculative software magic to infrastructure, labor and power. Once AI starts affecting utility bills, hiring plans, workplace surveillance, healthcare and military procurement, the conversation leaves demo-land and enters politics. That is when PR gets much less effective and scrutiny gets much more specific.
Why it matters: AI leaders want the upside of massive deployment without absorbing the backlash that deployment creates. That balancing act is getting shakier as the real-world footprint expands.
The Deets
- Altman said AI is being unfairly blamed for social and economic stress points
- Polling cited by AI Secret says 57% of voters now believe AI’s risks outweigh its benefits
- The broader backlash lands as leading AI firms pursue data center expansion, defense relationships, and deeper workplace automation
Key takeaway: AI is no longer just a technology story. It is becoming an accountability story.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Infrastructure play: A strategy focused on building the foundational systems, data centers, energy, and platforms that other products depend on.
🧰 Tools & Products
Claude, Computer, Bee, And The Great Agentification Of Everything
A handful of product updates point to the same broader shift: AI tools are being pushed beyond chat into systems that see, act, and operate software directly.
Anthropic updated Claude with embedded charts and diagrams in chat. Perplexity expanded its Computer agent to Pro users. Google added Gemini task automation on select smartphones. Bumble is introducing Bee, an AI assistant that learns preferences and suggests matches.
These are all different products, but they rhyme. The common idea is that AI should not just answer questions. It should work across apps, summarize context, execute steps, and make choices on your behalf. That is where things get convenient, and also where things get weird fast.
Why it matters: The industry is moving from chatbot novelty to action layers that sit on top of software and do the clicking for you.
The Deets
- Claude now generates interactive diagrams and charts inside conversations
- Perplexity Computer is available to Pro subscribers, with credits tied to usage
- Google Gemini can automate tasks on select smartphones by operating apps more directly
- Bumble's Bee aims to learn user preferences and privately recommend better matches
Key takeaway: AI products increasingly want a cursor, not just a text box.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Action layer: The part of an AI system that does not just generate text, but actually performs tasks across software or devices.
💸 Funding & Startups
Axiom Raises Big Money For AI That Can Actually Prove Things
Reasoning startup Axiom announced a $200M Series A at a valuation above $1.6B, with a focus on formal mathematics and verified AI. That is a notable signal in a market where plenty of money still flows to companies promising broader intelligence, broader agents, broader platforms and broadly hand-wavey outcomes. Axiom is aiming at something more constrained and, arguably, more defensible: systems that can reason in domains where correctness matters.
That matters because as AI gets deployed in technical, scientific, and safety-critical workflows, “sounds right” stops being good enough. Investors are increasingly interested in tools that do more than autocomplete confidence. Verified reasoning is one of the cleaner narratives for what comes after generic chatbots.
Why it matters: Money is still pouring into AI, but the sharper bets are shifting toward systems that can deliver reliability, not just fluency.
The Deets
- Axiom raised $200M
- The round values the company at more than $1.6B
- The startup focuses on formal mathematics and verified AI systems
Key takeaway: The next premium in AI may be trustworthiness, not just scale.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Verified AI: AI systems designed so their outputs or reasoning can be checked against formal rules, proofs, or other rigorous methods.
🔬 Research & Models
Recursive Self-Improvement Is Back On The Menu
At the Abundance Summit, Elon Musk said AI has already entered an early phase of recursive self-improvement, where newer systems help build the next generation and human involvement keeps shrinking. He suggested fully automated AI improvement could arrive as soon as this year or next. Musk being Musk, the timeline came with maximum voltage.
Even so, the claim lands because the underlying pattern is real enough to be worth watching. AI systems are already assisting with code generation, experiment design, evaluation, model tuning and tool use. That does not mean a full self-improving loop has arrived. It does mean parts of the stack are increasingly machine-assisted, which can compress development cycles whether or not you buy the grand theory.
Why it matters: Even partial self-improvement changes the tempo of the industry. Faster iteration means faster capability gains, faster deployment, and faster opportunities to make mistakes at scale.
The Deets
- Musk argued newer AI models are increasingly helping build successor systems
- He tied the trend to humanoid robotics such as Optimus
- He predicted machine intelligence plus automated labor could expand economic output dramatically over the next decade
Key takeaway: The self-improvement story may be overhyped, but the automation of AI development is becoming less hypothetical.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Recursive self-improvement: A scenario where AI systems help improve the very systems that come after them, creating a feedback loop of faster progress.
Robots Are Getting Better Hands, Better Muscles
Today’s robotics batch reads like a checklist of everything robots used to be bad at. A team at the University of Texas at Austin built FORTE, a robotic hand that can grip delicate objects like raspberries and potato chips without crushing them, thanks to soft robotics and air-pressure tactile sensing inspired by fish fins.
Researchers at Tohoku University developed a hair-thin actuator fiber that bends, twists, and contracts like an artificial muscle.
Meanwhile, the Allen Institute for AI introduced MolmoBot, an open manipulation system trained entirely in simulation and then transferred to real hardware.
Put together, these advances matter because useful robots need three things at once: dexterity, compliant movement, and enough training data to do something interesting outside a lab video. Soft hands help with fragile handling. Muscle-like fibers help with safer movement. Sim-trained systems help avoid the absurd cost of collecting every physical demonstration in the real world.
Why it matters: Robotics progress is starting to look less like isolated stunts and more like stack-building: better bodies, better sensors, better training pipelines.
The Deets
- FORTE achieved a 91.9% success rate handling delicate items and detected slip events with perfect precision
- Tohoku’s actuator fiber is produced with a thermal-drawing process similar to optical fiber manufacturing
- MolmoBot used 1.8M training trajectories generated in simulation and reached 79.2% success in real-world tasks
Key takeaway: The robot revolution remains annoyingly slow until suddenly it is not.
🧩 Jargon Buster - Sim-to-real: Training a robot in simulation and then transferring those learned skills to physical hardware in the real world.
The Security Story That Should Spook Every Enterprise AI Team
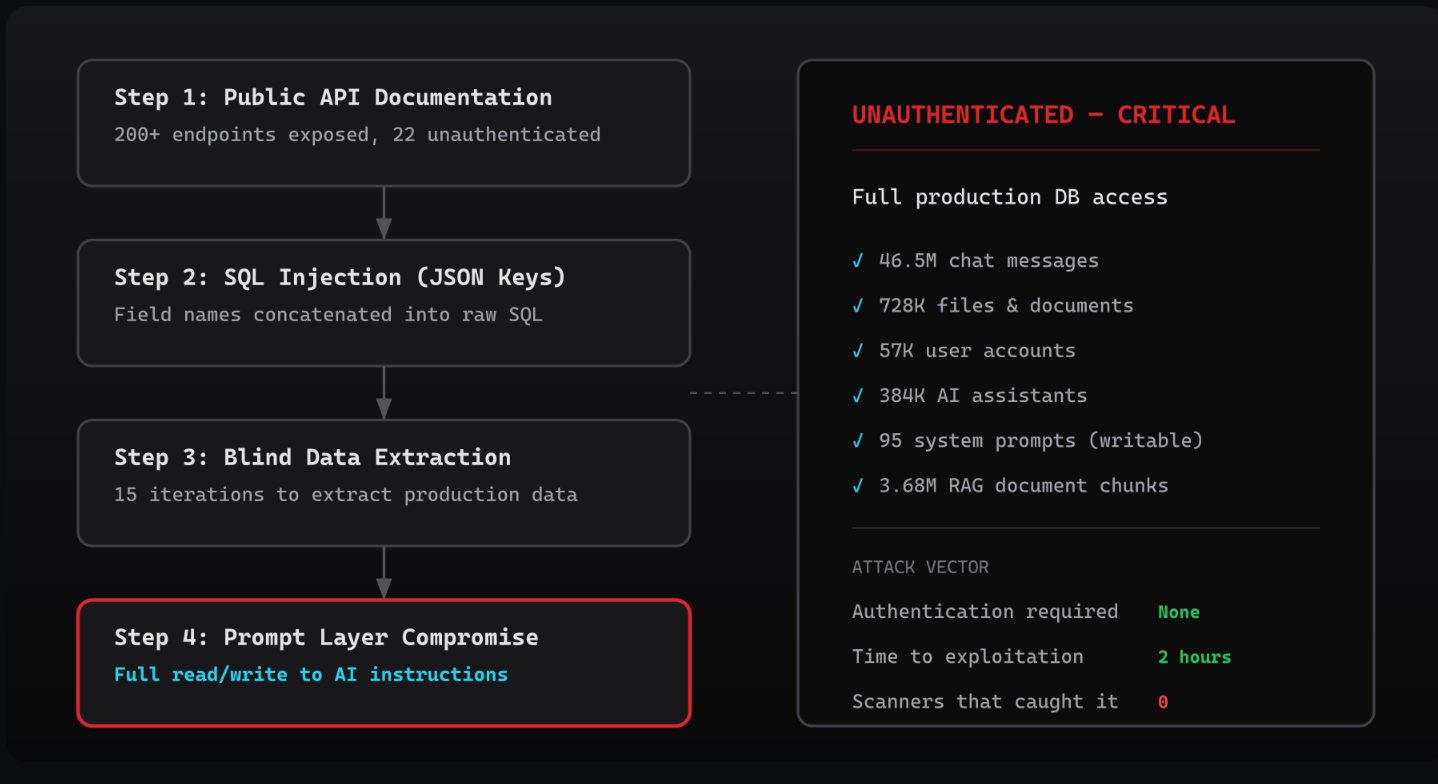
Security startup CodeWall said its AI agent hacked McKinsey’s internal AI chatbot Lilli in under two hours, finding exposed API docs and an authentication failure that led to broad database access. The reported haul was ugly: 46.5M messages, 728K files, 57K user accounts, and 95 control prompts, much of it in plain text.
McKinsey (the company that paid $600 million to settle investigations into its role in helping “turbocharge” opioid sales) says it was informed, investigated with a third party, found no evidence of other access, and patched the issue.
The alarming part is not just the scale. It is the banality. This was not some exotic frontier-model jailbreak involving mystical prompt kung fu. It was basic security hygiene failing around an internal AI system used by 70% of McKinsey staff, roughly 45K people, for client work. AI keeps introducing new interfaces, APIs, data flows, and permissions. If those old-school security controls do not keep up, “enterprise AI” starts to mean “a faster way to centralize risk.”
Why it matters: The AI boom is creating a large new attack surface, and some of it appears to be built with the same old mistakes in shinier packaging.
The Deets
- Lilli is used for chat, analysis, and search across 100K+ internal documents
- CodeWall said it found 22 endpoints that did not require authentication
- One exposed weakness reportedly enabled access to a database containing confidential messages, client files, and user accounts
Key takeaway: AI adoption without security discipline is just operational courage with extra steps.
🧩 Jargon Buster - API endpoint: A specific access point in a software system that lets other tools send requests or retrieve data.
⚡ Quick Hits
- Meta reportedly delayed its next AI model, Avocado, until at least May after internal evaluations found it underperforming against frontier rivals.
- xAI hired Andrew Milich and Jason Ginsberg from Cursor to strengthen Grok’s coding capabilities.
- OpenAI plans to integrate Sora into ChatGPT to drive usage as video competition heats up.
- Facebook Marketplace rolled out Meta AI features for auto replies, AI-generated listings, and seller profile summaries.
- A global Hexagon survey of 18,000 people across nine countries found fear of robots is highest where exposure is lowest.
- Coco Robotics unveiled Coco 2, a delivery robot designed for streets and bike lanes, using Niantic Spatial mapping tech built from more than 30B mapped images.
- Engineers at the University of Cincinnati built a dual-arm system to stabilize satellite repairs in microgravity by counterbalancing movement.
- Sharpa Robotics demonstrated a humanoid robot peeling an apple using MoDE-VLA, doubling baseline performance across four complex tasks.
- A German startup working in NATO-adjacent defense circles revealed AI-equipped cockroach scouts steered via neural stimulation for reconnaissance in tight spaces.
- A journalist sued Grammarly, alleging its “Expert Review” feature attached her name and views to AI suggestions she never approved.
🛠️ Tools of The Day
Google Workspace Studio - A practical automation layer for Gmail that can triage incoming mail, apply AI labels, extract invoice details, and send structured data into Sheets. This is the kind of tool that saves people from becoming full-time inbox janitors.
Claude - Anthropic’s assistant now supports embedded charts and diagrams inside chat, which makes explanations more visual and a lot less reliant on your imagination doing unpaid labor.
Perplexity Computer - Perplexity’s agent system is expanding to more users, pushing the company deeper into AI that can operate software rather than just answer questions about it.
Scrunch - A site-audit tool aimed at showing how AI interprets your website, with a focus on discoverability and customer reach in an AI-shaped internet.
Codex - OpenAI’s coding assistant added automations and themes, continuing the slow march toward “your IDE now has opinions.”
Today’s Sources: The Rundown AI, AI Secret, Robotics Herald
