Medicare To Use AI Deciders; Models Pass CFA; Mapping Polluters

Medicare Pilots AI Denials
Starting January 2026, Medicare will pilot WISeR (Wasteful and Inappropriate Service Reduction), an AI-driven prior authorization system that screens requests for certain procedures and can deny care deemed “low-value.” The program will run until 2031 in Arizona, Ohio, Oklahoma, New Jersey, Texas, and Washington.
Traditionally, Medicare has avoided heavy prior authorization, relying more on physician judgment. But WISeR moves it closer to the private insurance model, where AI has already been quietly making many approval decisions.
How this hits:
- For patients, routine care might get approved faster, but expensive or marginal procedures could face delays, denials, and lengthy appeals. Critics warn this could result in avoidable harm, worsened outcomes, and inequities.
- For providers, WISeR adds administrative friction — forcing doctors to practice medicine inside algorithmic guardrails rather than their own judgment.
- For the system, CMS argues the shift will cut fraud, waste, and abuse, preserving Medicare dollars as the population ages.
The deets:
- The AI will initially focus on procedures like skin/tissue substitutes, electrical nerve stimulator implants and knee arthroscopy - areas flagged as prone to overuse.
- CMS insists “qualified human clinicians” must review denials and that vendors cannot be paid based directly on denial rates.
- Still, vendors share in “savings” from reduced spending, creating strong incentives to limit costly care. Hospital groups call this a built-in conflict of interest.
- The move comes just days after the Trump administration told private insurers to scale back prior authorization, a contradiction that left lawmakers calling the government’s message “talking out of both sides of their mouth.”
Pushback:
- Physicians: Surveys by the AMA show 61% of doctors believe AI has already increased denials, worsening harms. Past investigations found private insurers spending as little as 1.2 seconds per case on “human review.”
- Lawmakers: Rep. Suzan DelBene (D-WA) called the program “hugely concerning,” while Rep. Greg Murphy (R-NC), a physician, said insurers already deny too much care — and now Medicare risks repeating the mistake. A bipartisan House measure seeks to block WISeR’s funding.
- Policy experts: Researchers argue Medicare is creating a “regulatory blind spot” by outsourcing medical judgment to algorithms. Jennifer Oliva of Indiana University warns insurers - and now Medicare - may rely on algorithms to delay appeals until patients die, reducing payouts.
Zooming out:
- Private insurers like Cigna and UnitedHealthcare already deploy AI in prior authorization. They insist humans have final say, but lawsuits claim denials are largely automated.
- Public sentiment is strongly negative: a KFF poll found nearly three-quarters of Americans think prior authorization is a major problem.
- AI Secret frames WISeR as Medicare “weaponizing automation” - scaling not just savings, but denials.
Key takeaway:
Medicare is stepping into uncharted territory - replacing physician discretion with algorithmic gatekeeping. The WISeR pilot could save billions, but also risks making access to care hinge on a model’s threshold rather than a doctor’s call. Whether this pilot reduces waste or entrenches a denial-by-default culture will define its legacy.
Read more: NBC News, AI Secret
AI Passes The CFA - Essays Included
NYU Stern and GoodFin tested 23 models on mock CFA Level III exams (the tough ones): Nine passed.
OpenAI o4-mini topped 79.1% on essays; Gemini 2.5 Pro and Claude 4 Opus landed 75.9%/74.9%.
Tasks that take humans ~1,000 hours across three levels took models minutes. Graders rated AI essays +5.6 points higher than automated systems.
Translation: reasoning models now handle structured, written analysis, pushing humans toward client trust, context and judgment as the differentiation.
Read more: The Rundown
Developers Use AI Constantly (But Don’t Quite Trust It)
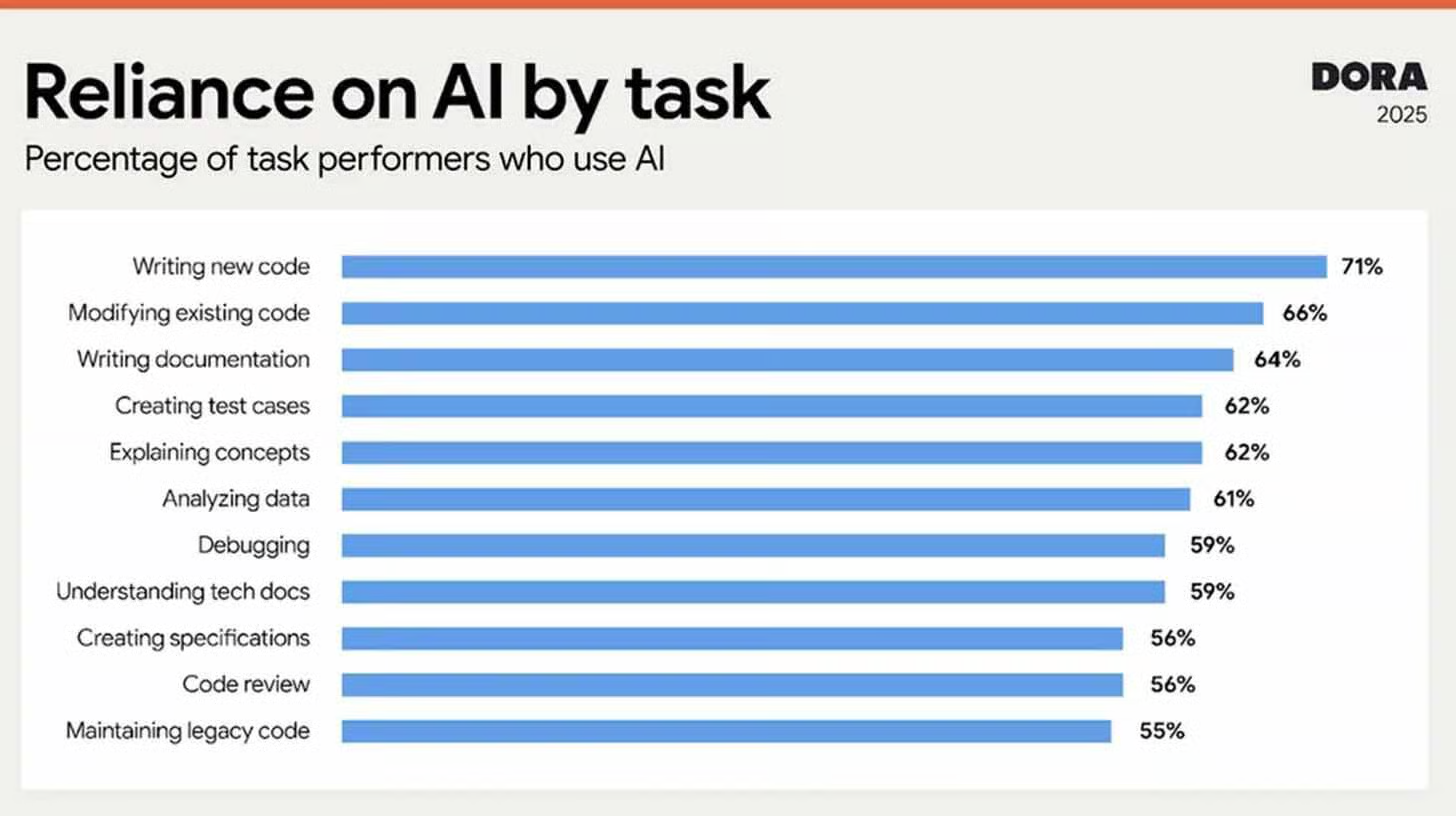
Google Cloud’s new DORA report (on the ‘State of AI-assisted Software Development’) pegs AI adoption at ~90% among devs, with respondents spending about two hours/day in assistants.
The paradox: 30% trust AI outputs only “a little” or “not at all.” Yet 80% report productivity gains and 59% see improved code quality.
Google’s new DORA AI Capabilities Model outlines seven practices (think: review gates, evals and safe rollout patterns) to dial benefits up while keeping humans as the quality control. In short: use the turbo, but keep a hand on the wheel.
Read more: The Rundown
MIT Steers Generative AI Toward Quantum Materials
MIT (with Google DeepMind) released SCIGEN, which forces geometric rules into diffusion models so generations aren’t just pretty - they’re physically plausible. Read: Creating materials with quantum properties.
From 10M candidates, 1M looked stable; two were synthesized in the lab with the predicted magnetic behavior. It’s a template for “design → simulate → build”: fewer dead ends, more lab-ready ideas.
Read more: The Rundown
AI Map Exposes 660M Pollution Sources

Climate Trace, co-founded by Al Gore, launched an AI map that fuses satellites, sensors, and emissions databases to track fine particulate pollution from 660M+ sources (power, steel, shipping, etc.). Think: near-real-time visibility that makes non-compliance harder to hide - for regulators, investors, and communities alike.
Read more: AI Secret
🚀 NewsBits & Launches
- Microsoft 365 Copilot now includes Anthropic Claude as a model option- first partner beyond OpenAI in that stack.
- SAP × OpenAI announced “OpenAI for Germany” to bring sovereign AI to the public sector by 2026.
- Cohere raised $100M (near $7B valuation) on enterprise demand for North and Command A.
- Cloudflare open-sourced VibeSDK for roll-your-own vibe coding platforms.
- U.K. Fraud Risk Accelerator (AI) reportedly recovered £480M in a year - evidence that targeted agentic tooling can move real money.
- Kling 2.5 Turbo - A high-quality video generator tuned for speed and consistency on complex motion and multi-shot prompts. Good for social spots and product demos where turnaround matters.
- Mixboard (Google Labs) - An experimental Gemini-powered canvas for moodboards; type or talk through ideas and it composes visual directions you can iterate. Handy for brand explorations or creative brief kickoffs.
- Qwen3-VL - Alibaba’s new vision-language model aiming at strong grounding and document/UI understanding. Useful for screenshots, charts, receipts, and layout-heavy tasks.
- Sprinto (Questionnaire Copilot) - Answers security questionnaires in minutes from your knowledge base. Ideal if sales cycles stall on vendor risk.
- Manna 2.0 - A Bible study app upgrade with multilingual chat, a lighter AI companion, and new learning flows. A niche, but good signal of verticalized AI UX.
- Memories.ai - “Perplexity for videos” that analyzes why clips go viral and predicts trends; useful for creative briefs and A/B concepts.
- Conduit AI - Builds conversational agents for a unified inbox (email, chat, support) that learn over time. Think tier-1 triage that doesn’t forget.
- Pine AI - Customer service assistant aimed at deflection and quality, with tools for handoff and compliance.
- Heardly - “Read best books fast” summaries; good for ideation, but use critical thinking—hallucinated citations remain a known risk across summary apps.
- CopyOwl - Research agent for deep-dive briefs; pairs nicely with human fact-checking when stakes are high.
- Flot AI - A cross-app assistant that writes, reads, and remembers context across your desktop—useful for glue work and snippet reuse.
Today’s Sources:
The Internet
AI Secret
The Rundown AI
